My Fast.ai Lesson 1 of Course 22
A walkthrough of the steps taken to run Fast.ai lesson 1 of Course 22
A walkthrough of my attempt to run the Fast.ai Lesson 1, Is it a bird? Creating a model from your own data from course 22 on Kaggle.
Create a copy of the notebook
The first step was to create a copy of the notebook. A click on the “Copy & Edit” button creates the copy.
Internet setup
The first codeblock checks if you’ve configured your kaggle account to access the internet. This is possible if you have linked a valid phone number. I had already done this step prior at some point before when I attempted the course.
#NB: Kaggle requires phone verification to use the internet or a GPU. If you haven't done that yet, the cell below will fail
# This code is only here to check that your internet is enabled. It doesn't do anything else.
# Here's a help thread on getting your phone number verified: https://www.kaggle.com/product-feedback/135367
Upgrade latest version of the libraries
This step upgrades the latest version of the fastai and duckduckgo_search
libraries. There’s also a note to indicate that warnings are expected. As
suggested I see the following warnings which I ignore.
Broken function to search for images
The first section of code is to download bird pictures. This is done by defining
a function search_images. This function fails. At first I follow the note
mentioned above the call and try running the cell a couple of times.
#NB: `search_images` depends on duckduckgo.com, which doesn't always return correct responses.
# If you get a JSON error, just try running it again (it may take a couple of tries).
urls = search_images('bird photos', max_images=1)
urls[0]
I keep getting the following error which leads me to believe the code is broken.
The warning states that ddg_images is deprecated.
Searching for 'bird photos'
/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/duckduckgo_search/compat.py:60: UserWarning: ddg_images is deprecated. Use DDGS().images() generator
warnings.warn("ddg_images is deprecated. Use DDGS().images() generator")
/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/duckduckgo_search/compat.py:64: UserWarning: parameter page is deprecated
warnings.warn("parameter page is deprecated")
/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/duckduckgo_search/compat.py:66: UserWarning: parameter max_results is deprecated
warnings.warn("parameter max_results is deprecated")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HTTPStatusError Traceback (most recent call last)
/tmp/ipykernel_18/2432147335.py in <module>
1 #NB: `search_images` depends on duckduckgo.com, which doesn't always return correct responses.
2 # If you get a JSON error, just try running it again (it may take a couple of tries).
----> 3 urls = search_images('bird photos', max_images=1)
4 urls[0]
/tmp/ipykernel_18/1717929076.py in search_images(term, max_images)
4 def search_images(term, max_images=30):
5 print(f"Searching for '{term}'")
----> 6 return L(ddg_images(term, max_results=max_images)).itemgot('image')
/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/duckduckgo_search/compat.py in ddg_images(keywords, region, safesearch, time, size, color, type_image, layout, license_image, max_results, page, output, download)
80 type_image=type_image,
81 layout=layout,
---> 82 license_image=license_image,
83 ):
84 results.append(r)
/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/duckduckgo_search/duckduckgo_search.py in images(self, keywords, region, safesearch, timelimit, size, color, type_image, layout, license_image)
425 cache = set()
426 for _ in range(10):
--> 427 resp = self._get_url("GET", "https://duckduckgo.com/i.js", params=payload)
428 if resp is None:
429 break
/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/duckduckgo_search/duckduckgo_search.py in _get_url(self, method, url, **kwargs)
87 logger.warning(f"_get_url() {url} {type(ex).__name__} {ex}")
88 if i >= 2 or "418" in str(ex):
---> 89 raise ex
90 sleep(3)
91 return None
/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/duckduckgo_search/duckduckgo_search.py in _get_url(self, method, url, **kwargs)
81 if self._is_500_in_url(str(resp.url)) or resp.status_code == 202:
82 raise httpx._exceptions.HTTPError("")
---> 83 resp.raise_for_status()
84 if resp.status_code == 200:
85 return resp
/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/httpx/_models.py in raise_for_status(self)
747 error_type = error_types.get(status_class, "Invalid status code")
748 message = message.format(self, error_type=error_type)
--> 749 raise HTTPStatusError(message, request=request, response=self)
750
751 def json(self, **kwargs: typing.Any) -> typing.Any:
HTTPStatusError: Client error '403 Forbidden' for url 'https://duckduckgo.com/i.js?l=wt-wt&o=json&s=0&q=bird%20photos&vqd=4-120798375579229292297400223005060697795&f=%2C%2C%2C%2C%2C&p=1'
For more information check: https://httpstatuses.com/403
Ok, looks like there’s some help in the comments for the original kaggle notebook. This
comment solves the issue by installing the fastbook package and
redefining the search_images with a an implementation which uses
search_images_ddg from the fastbook package. Thank you Kevin Graziani.
So adding the following codeblock to install fastbook
if iskaggle:
!pip install -Uqq fastbook
And redefining search_images with the following codeblock. (I wonder why the
from fastai.vision.widgets import * statement is required? )
from fastbook import *
from fastai.vision.widgets import *
def search_images(term, max_images=30):
print(f"Searching for '{term}'")
return L(search_images_ddg(term, max_images=max_images))
The search_images_ddg function can be seen in the fastbook/utils.py file
on github. There’s also a search_images_bing funtion, which I should try out
in my assignment work.
With the issue solved I’m able to download the bird URL.
And download the image
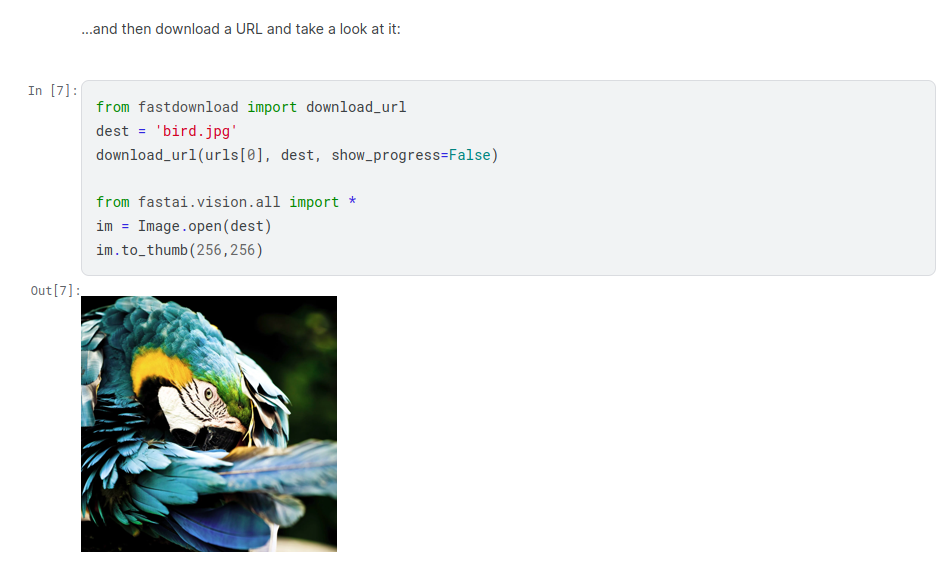
The function download_url is from the fastdownload.core module. It downloads
a single URL to a destination path.
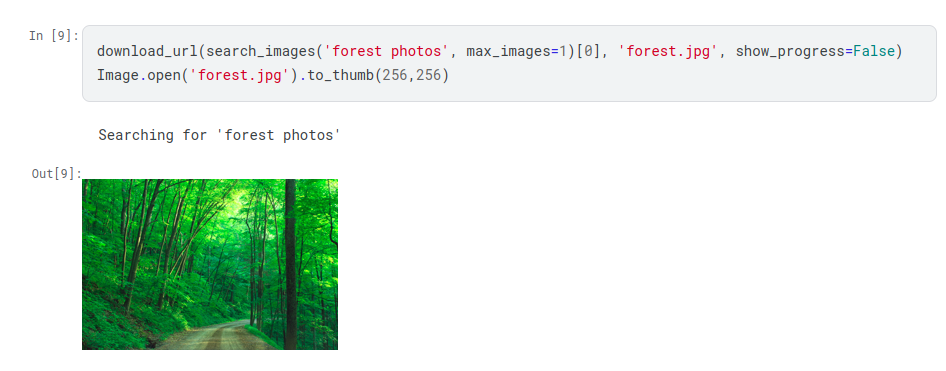
For the forest photo search the download_url and search_images function is
combined into a single statement followed by the Image.open function:
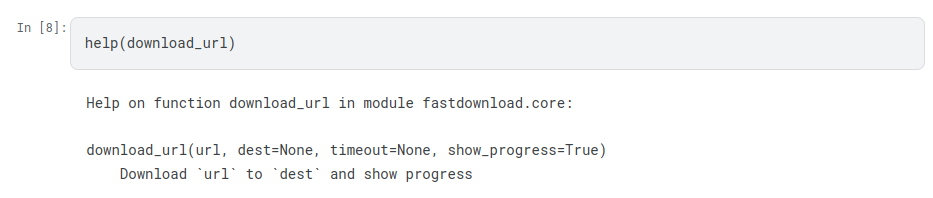
Using help
The help function can be used to get some documentation and information about
the module in which a specific function is defined.
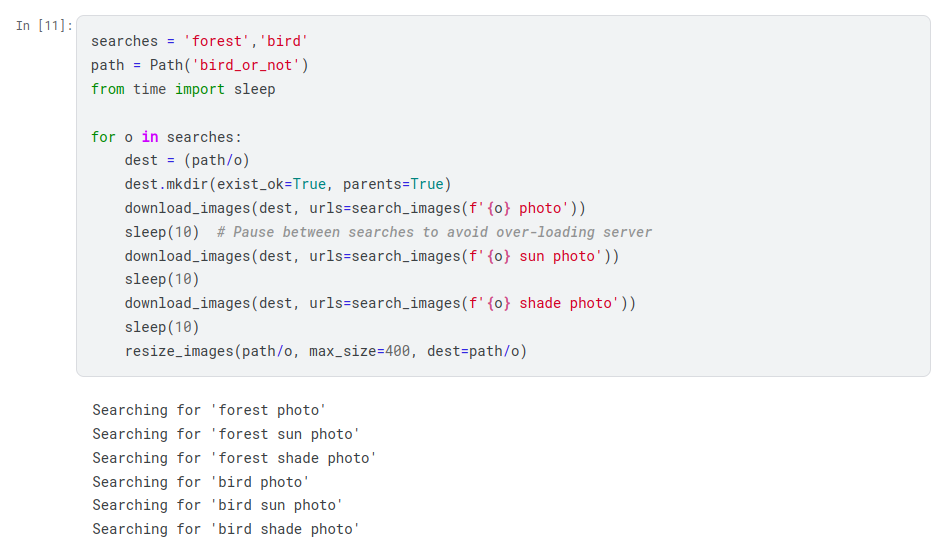
Download Images
After verifying that our search results are reasonable we can download the
images for bird and forest. In order to do so the download_images function
from the module fastai.vision.utils module is used. Each search is combined
with lighting description like sun and shade to get images of birds and
forest with different lighting conditions. The search_images has its
max_images set to 30 so we get 90 images for bird and forest respectively.
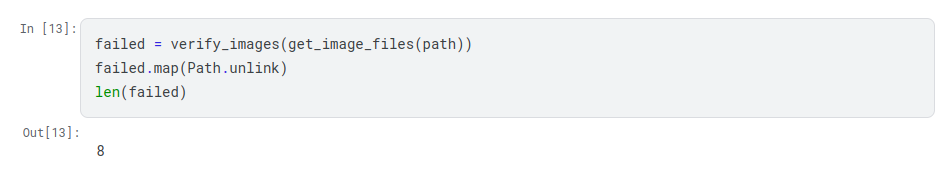
Verify images
The second stage starts with removing images that can’t be opened. To do so we
use the verify_images function from the fastai.vision.utils module. In my
run 8 images were broken so it gets unlinked. This step is required to make sure
our training set is valid.
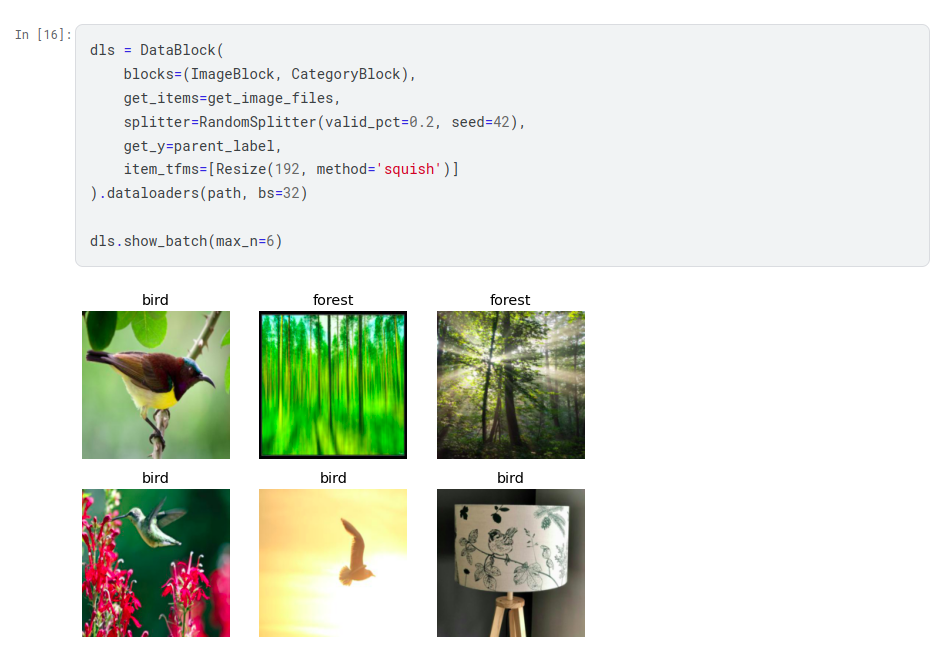
DataBlocks and DataLoaders
Next we need an object based on DataLoaders which is obtained from the
DataBlock object. Think of this as the set of data used for training and the
set used for validation. The DataBlock object is defined in the
fastai.data.block module. This object is important as it is used to define
different types of data sets. The DataBlock is sort of a factory class that
can be used to define the main things that change in each model.
The initialization of DataBlock has several parameters:
blocks, categorizes the type of inputs and outputs. In this example the inputs are images henceImageBlockand the outputs are categories henceCategoryBlock.get_items, specifies how the inputs are to be retrieved.splitter, how the data is to be split into training and validation sets. Validation is important to determine the effectiveness of training.get_y, defines how to get the categories for input items. In this example it is the parent directory i.e. bird or forest.item_tfms, specifies what procedure to use to adjust the input data for training. Most computer vision models require the input to be of a fixed size. In this example we’re resizing the images to be 192x192 and if it doesn’t fit we want them to be “squished”.
Traiing of a model typically is done on a GPU. Pytorch uses DataLoaders to
feed batches of the data set for training cycles.
To inspect the Dataloader we use the show_batch function. This should display
the input data and categories if everything is defined correctly.
More information about construction of a DataBlock is available in the Data
Block Tutorial or in the Data Block API docs
Train the model
In order to train the model the vision_learner function is used to create a
learner. The resnet18 computer vision model is used which can be trained on a
CPU. The fine_tune function is a helper function that uses the best practices
to tune the model.

Test the model
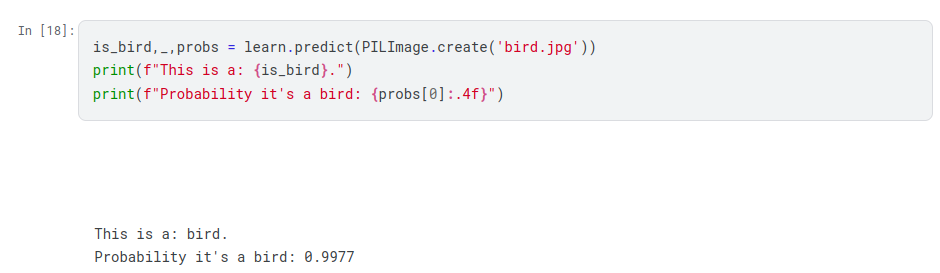
The final step is to see if it can predict whether an image has a bird or not.